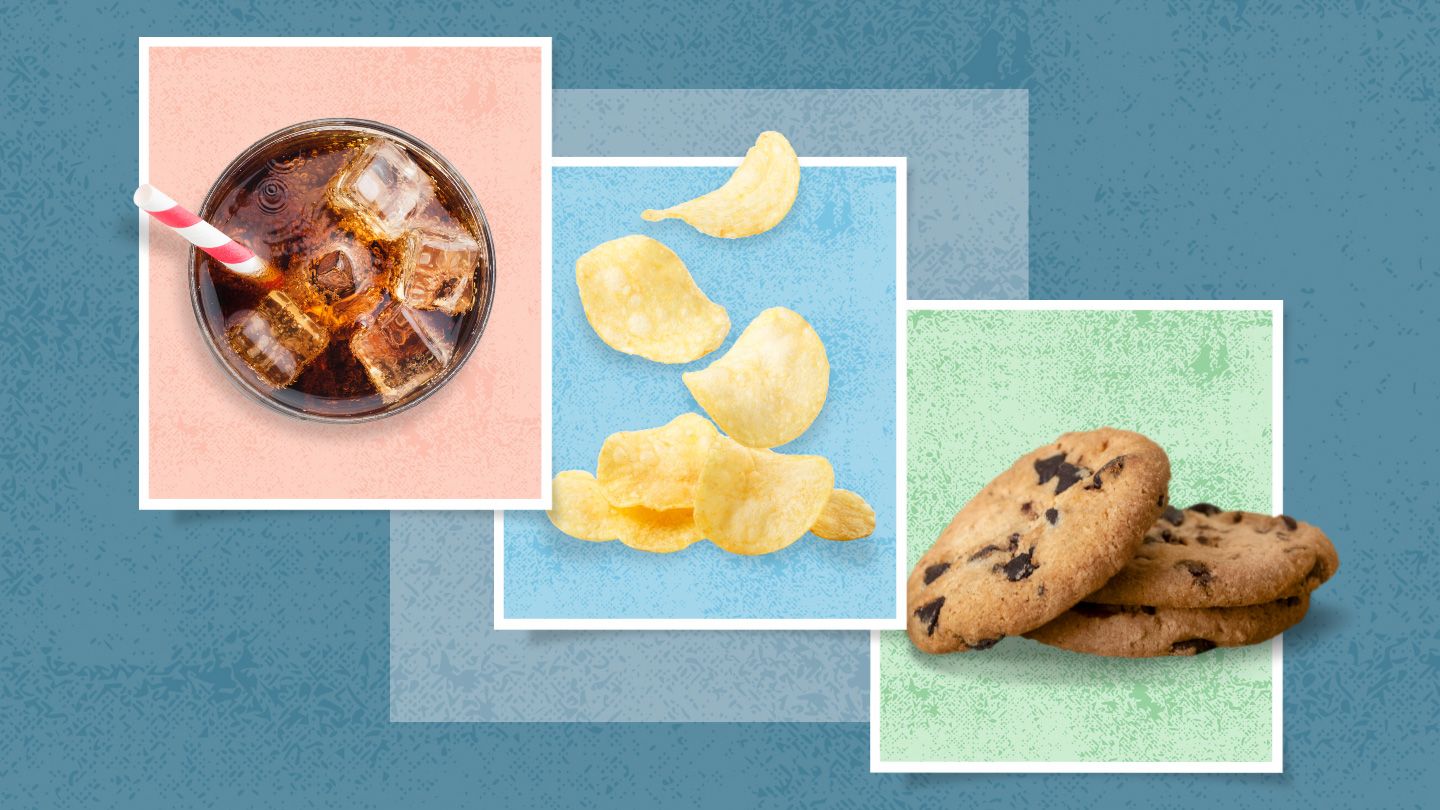
If those plant-based foods are ultra-processed, however, they may do more harm than good when it comes to heart health.
A new study indicates that excessive consumption of plant-based ultra-processed foods — including certain frozen pizzas, breakfast cereals, salty snacks, and packaged breads, pastries, and cookies — may heighten the risk of heart disease by up to 5 percent and the risk of death from heart disease by as much as 12 percent.
Conversely, researchers found that participants who increased their intake of non-ultra-processed plant-sourced food by 10 percent had a 7 percent lower risk of cardiovascular disease and a 13 percent reduced risk of death from cardiovascular disease.
“Our main finding is that a plant-based diet can improve your cardiovascular health, as long as it does not rely on ultra-processed foods,” says the lead study author, Fernanda Rauber, PhD, a researcher with the Center for Epidemiological Research in Nutrition and Health at the University of São Paulo School of Public Health in Brazil. “As more people adopt plant-based diets, it becomes crucial to examine the role of food processing within these dietary patterns, particularly concerning cardiovascular diseases.”
“The study challenges the common perception that plant-based foods are inherently healthier,” says Janna Assar, MD, a family medicine physician with Banner Health in Phoenix. “It underscores that the high level of processing can negate the potential benefits of plant-based foods, highlighting the need to consider food processing in dietary guidelines, not just the origin of the food.”
Ultra-Processed Foods Threaten Heart Health
Ultra-processed foods are often industrial formulations created by breaking down whole foods into chemical components, modifying them, and then combining them with additives, according to Dr. Rauber.
She and her collaborators stress that processed plant-based foods with a high content of unhealthy fats, sodium, and added sugars can contribute to dyslipidemia (abnormal levels of fat in the bloodstream), atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, insulin resistance, obesity, and metabolic disorders like diabetes.
Some of these plant-based foods may also contain preservative chemicals and artificial sweeteners and food coloring, as well as contaminants from industrial processing that may raise heart risks.
Christopher Gardner, PhD, the chair of the American Heart Association’s Nutrition Committee of the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health, points out that just because foods are packaged doesn’t necessarily make them unhealthy.
He suggests that consumers check nutrition labels found on most packaged goods, and look for products that are high in fiber and other nutrients (such as vitamins, minerals, unsaturated fat, and protein), but low in saturated fat, added sugars, and sodium.
“While it’s always best to select fresh, whole foods that don’t come in packages that require a nutrition label, we know that this isn’t possible for everyone at all times,” says Dr. Gardner, who is also a professor of medicine at Stanford University in California.
What About Fake Meat?
In this study, these types of foods only accounted for 0.2 percent of total calories consumed, so specific conclusions could not be made related to this kind of product. Also, many meat alternatives, such as the recently popular Impossible Burgers and Beyond Meat, were not yet on the market when this data was collected.
On the other hand, Dr. Assar warns that certain fake meats may also contain added sodium, unhealthy fats, and various additives to mimic the taste and texture of meat. “The processing methods and ingredients used can contribute to negative health outcomes,” says Assar, who was not involved in this study.
The Case Against Ultra-Processed Foods Grows
Because this was an observational analysis, it could not establish cause and effect. Rauber and her team emphasize that the study only established an association between heart diseases and the consumption of plant-sourced ultra-processed foods.
Moreover, it’s possible that participants inaccurately reported the types and amounts of foods they consumed, or that their lifestyle factors contributed to these findings.
Still, Rauber notes that this latest research adds to a growing body of evidence indicating that ultra-processed foods can lead to negative health outcomes. A review of 45 prior scientific analyses on the topic concluded that greater exposure to ultra-processed foods raised the likelihood of death from preventable diseases.
“I suggest basing your diet primarily on whole and minimally processed foods,” she says. When buying ready-made food or preparations, the best tip is to read the ingredient list. If it contains only ingredients you recognize and commonly have in your kitchen, it is most likely made from real food and is not an ultraprocessed food.”



Post Comment