Public health is a vital aspect of any society. It is the science of protecting and improving the health of entire populations. In developing nations, public health challenges are enormous, mainly due to poor healthcare infrastructure, limited resources, inadequate access to essential medical supplies, and insufficient knowledge. Improvements in public health require significant investments in healthcare interventions that can help prevent and manage diseases, reduce morbidity and mortality rates, and enhance the quality of life for citizens. This article will explore the importance of healthcare interventions in developing nations for public health.
What Are Healthcare Interventions?
Healthcare interventions refer to a wide range of techniques and measures that aim to promote, protect, restore, or maintain health in individuals or communities. These interventions include preventative measures such as immunization campaigns, health education programs, and awareness-raising efforts. They also involve curative measures such as treatment plans, surgeries, and medical interventions that aim to improve or manage existing health conditions. Healthcare interventions can also be rehabilitative, such as physiotherapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy.
In developing nations, healthcare interventions play a critical role in addressing the burden of disease. For example, vaccination campaigns have been successful in reducing the incidence of infectious diseases such as polio, measles, and tetanus. Similarly, education campaigns have been instrumental in promoting healthy behaviors such as hand hygiene, safe sex practices, and healthy eating habits.
Why Are Healthcare Interventions Important for Public Health in Developing Nations?

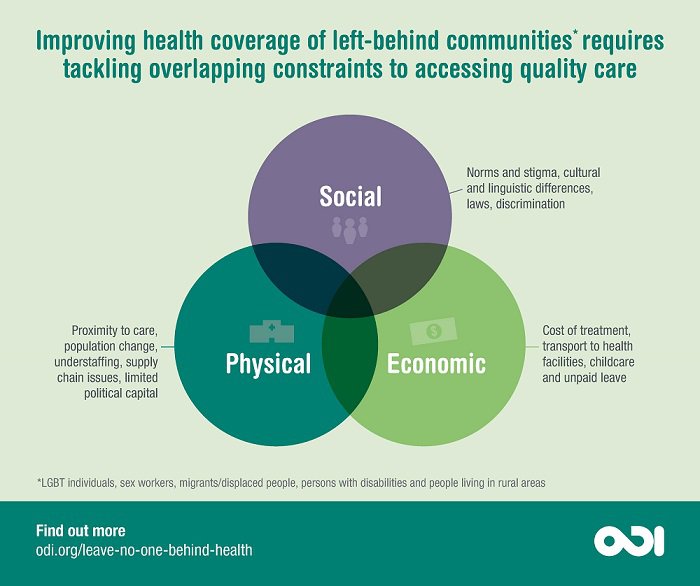
Developing nations face significant public health challenges, including high rates of infant and maternal mortality, communicable diseases, malnutrition, and non-communicable diseases (NCDs). Healthcare interventions offer a cost-effective approach to address these issues by providing affordable and accessible healthcare services to those who need them most.
One of the primary benefits of healthcare interventions is their ability to prevent diseases from spreading. For example, immunization campaigns can help reduce the spread of infectious diseases by creating herd immunity among the population. Similarly, health education programs can promote healthy behaviors that reduce the risk of contracting and spreading diseases.
Healthcare interventions can also save lives by providing timely medical care to those in need. In developing nations where access to healthcare services is limited, healthcare interventions can make a significant difference in mortality rates. For example, maternal and child health interventions can provide critical care to pregnant women and newborns, reducing the risk of complications and death.
Examples of Healthcare Interventions in Developing Nations
Several healthcare interventions have been implemented successfully in developing nations to address public health challenges. Here are some examples:
Vaccination Campaigns
Vaccination campaigns are one of the most effective public health interventions for preventing infectious diseases. In developing nations, vaccination campaigns have helped to control the spread of diseases such as polio, measles, and tetanus. These campaigns involve the administration of vaccines to large populations, usually through mass vaccination drives.
Health Education Programs
Health education programs aim to promote healthy behaviors and practices that can reduce the risk of disease. These programs include awareness-raising campaigns, school-based health education, and community health promotion activities. They can cover a wide range of topics, from hand hygiene to safe sex practices and healthy eating habits.
Maternal and Child Health Interventions
Maternal and child health interventions aim to provide essential healthcare services to pregnant women and newborns. These interventions include prenatal care, delivery services, postnatal care, and neonatal care. They help reduce the risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth and improve the health outcomes of mothers and infants.
HIV/AIDS Interventions
HIV/AIDS interventions aim to prevent the spread of HIV/AIDS and provide care and support to those affected by the disease. These interventions include awareness-raising campaigns, condom promotion, HIV testing and counseling, and antiretroviral therapy. They help reduce the incidence of HIV/AIDS and improve the quality of life of those living with the disease.
The Challenges of Implementing Healthcare Interventions in Developing Nations

While healthcare interventions offer significant benefits for public health in developing nations, implementing them can be challenging. Some of the challenges include:
Limited Resources
Developing nations often have limited resources to invest in healthcare interventions. This can limit the scope and scale of healthcare programs and make it difficult to reach underserved populations.
Inadequate Healthcare Infrastructure
In many developing nations, healthcare infrastructure is inadequate, with a scarcity of medical facilities, equipment, and trained healthcare professionals. This makes it challenging to implement and sustain healthcare interventions effectively.
Cultural and Social Factors
Cultural and social factors can also impact the success of healthcare interventions. For example, some cultural beliefs and practices may discourage people from seeking medical care or following prescribed treatment plans.
Conclusion
Healthcare interventions are critical for addressing public health challenges in developing nations. They offer a cost-effective approach to prevent and managediseases, reduce morbidity and mortality rates, and improve the quality of life for citizens. Vaccination campaigns, health education programs, maternal and child health interventions, and HIV/AIDS interventions are just a few examples of successful healthcare interventions that have been implemented in developing nations.
However, implementing healthcare interventions in developing nations can be challenging due to limited resources, inadequate healthcare infrastructure, and cultural and social factors. Despite these challenges, investing in healthcare interventions is essential to improving public health outcomes and promoting equitable access to healthcare services.
In conclusion, healthcare interventions play a vital role in addressing public health challenges in developing nations. By investing in healthcare interventions, governments and organizations can significantly improve the health outcomes of their populations, reduce healthcare costs, and promote sustainable development.