Introduction:
Monkeypox is a rare viral disease that occurs primarily in central and western Africa. The monkeypox virus is related to the virus that causes smallpox in humans.
Monkeypox was first identified in 1970 among laboratory monkeys. Since then, a limited number of cases have been reported in humans in Africa and Europe. Most of the cases have occurred in people who have had contact with infected animals, such as pet monkeys, Gambian giant rats, and squirrels.
In this article, we will discuss the symptoms of monkeypox, treatment options, and ways to prevent the disease.
What is monkeypox?
Monkeypox is a rare disease that is caused by a virus.
The monkeypox virus is related to the virus that causes chickenpox and smallpox. It is believed that monkeypox first came to the United States when people who had been in Africa contracted it.
Monkeypox can cause fever, headache, muscle aches, and tiredness. It can also cause a rash, blisters, and swelling of the face. In some cases, monkeypox can lead to death.
There is no specific treatment for monkeypox, but people who are infected can be treated with antibiotics and other supportive care. There is also a vaccine available for monkeypox.
The best way to prevent monkeypox is to get vaccinated against it.
How is monkeypox spread?
Monkeypox is spread through contact with the skin, mucous membranes, or bodily fluids of an infected person.
It can also be spread through contact with objects or surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. In some cases, the virus can be spread through close contact with infected animals, such as monkeys, which is how the disease got its name.
Person-to-person transmission of monkeypox is rare, but can occur in close contacts of an infected person, such as family members or healthcare workers.
What are the symptoms of monkeypox?
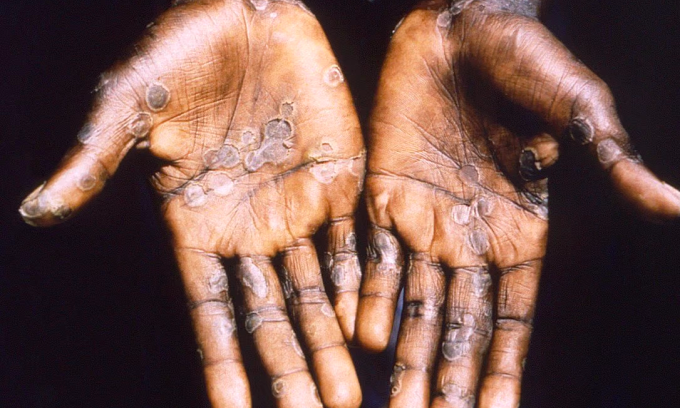
The symptoms of monkeypox can vary from person to person, but typically include fever, headache, and a rash. The rash is usually the most distinctive sign of the virus, and can develop anywhere on the body. It starts as small red bumps that grow into pus-filled lesions.
If you think you may have contracted monkeypox, it’s important to seek medical attention right away. There is no specific cure for the virus, but early diagnosis and treatment can help reduce the severity of symptoms. There is also a vaccine available for monkeypox, so it’s important to get vaccinated if you’re traveling to an area where the virus is present.
How is monkeypox treated?
There is currently no cure for monkeypox, so treatment focuses on relieving symptoms. This may include fluids, antibiotics to prevent or treat infection, pain relief, and oxygen therapy if needed. Early diagnosis and treatment is vital for the best possible outcome.
There are a few different ways to prevent monkeypox. The most important is to vaccinate against it, as this offers the best protection. Other precautions include avoiding contact with infected animals or people, washing hands regularly, and avoiding unprotected close contact with anyone who’s sick.
Can monkeypox be prevented?
Yes, monkeypox can be prevented. The best way to prevent monkeypox is to avoid contact with animals that may be infected, such as primates, bats, and rodents. There is also a vaccine available for people who may be at risk for monkeypox, such as healthcare workers and laboratory personnel.
What are the long-term effects of monkeypox?
Monkeypox is a rare disease that can have serious long-term health effects, including neurological problems, deafness, and eye problems.
In some cases, monkeypox can also lead to death. The long-term effects of the virus can be unpredictable and vary from person to person. Make sure you seek medical attention if you think you may have contracted monkeypox, as early diagnosis and treatment is essential for minimizing the chances of long-term health complications.
Conclusion:
Monkeypox is a rare viral disease that occurs in humans. It is caused by a virus that is similar to the virus that causes chickenpox and smallpox. Monkeypox is usually a mild disease, but it can cause serious illness in some people. Symptoms of monkeypox include fever, headache, muscle aches, and exhaustion. A rash may develop on the face, chest, and back.
Introduction:
Monkeypox is a rare, serious, and sometimes fatal disease caused by a virus. It is found mainly in central and West Africa, but has been reported in other parts of the world. Monkeypox is spread from contact with an infected animal, most often a monkey or squirrel.
Initial symptoms of monkeypox include fever, headache, muscle aches, and exhaustion. A rash develops on days 3-5 after the fever starts, and can spread to the entire body.
There is no specific treatment for monkeypox, but people with the disease are often treated for malaria or other infections. There is no vaccine available for monkeypox.
In this post, we will discuss the symptoms of monkeypox, treatment options, and ways to prevent the disease.
What is monkeypox?
Monkeypox is a rare, yet potentially deadly disease that is caused by a virus.
The monkeypox virus is closely related to the smallpox virus, which was eradicated in the 1970s. Symptoms of monkeypox include fever, headache, muscle aches, and swollen lymph nodes.
In some cases, people who have contracted monkeypox can develop a rash that spreads over their entire body. This rash can lead to blisters and ulcers, which can eventually lead to death if not treated properly.
There is no specific cure for monkeypox, but it can be treated with antibiotics and antiviral drugs. The best way to prevent monkeypox is to get vaccinated against it.
How is monkeypox spread?
Monkeypox is a virus that is spread through contact with an infected animal or person.
The monkeypox virus is found in Africa and can be spread to people through contact with infected animals, such as rodents, Gambian giant rats, and monkeys. The virus can also be spread to people through contact with an infected person, such as exposure to respiratory droplets or lesions.
There is no specific treatment for monkeypox, but it can be treated with supportive care. Prevention of monkeypox includes prompt diagnosis and treatment of any symptoms, prompt isolation of infected people, and vaccination against monkeypox.
What are the symptoms of monkeypox?
The symptoms of monkeypox generally develop within 10 days of exposure to the virus and can include fever, headache, muscle aches, and exhaustion. A rash will often develop around day 5-7 after the appearance of other symptoms and can look like blisters or pimples. The rash usually starts on the face and spreads to other parts of the body. Other symptoms can include swollen lymph nodes, mouth ulcers, and diarrhea.
If you have any of these symptoms, we recommend seeking medical attention as soon as possible. Monkeypox is a serious illness and can be fatal if not treated.
How is monkeypox treated?
There is no specific treatment for monkeypox, however, it is usually treated with antibiotics, antivirals, and supportive care. Some people may also require hospitalization.
Can monkeypox be prevented?
Monkeypox is a viral disease that is most commonly spread through contact with infected animals, though it can also be spread through contact with contaminated objects or materials.
There is currently no vaccine available to prevent monkeypox and no specific treatment for the disease. However, treatment is focused on relieving symptoms and supporting the patient’s health.
The best way to protect yourself from monkeypox is to avoid contact with infected animals and materials.
What are the long-term effects of monkeypox?
Monkeypox is a viral disease that is closely related to smallpox. It is a rare disease that is most commonly found in central and western Africa. While the symptoms of monkeypox are very similar to those of smallpox, it is much less deadly.
There is currently no cure for monkeypox, but treatment options are available to help reduce the symptoms and make the person more comfortable. There is also a vaccine for monkeypox, which can help prevent people from getting the disease.
The long-term effects of monkeypox are not yet known, but it is likely that they will be similar to those of smallpox.
Conclusion:
Monkeypox is a rare but serious viral illness that can cause severe health problems. It is related to chickenpox and smallpox, and is mainly found in central and western Africa. There is no specific treatment for monkeypox, and it is important to get medical help if you think you or someone you know might have it. There is a vaccine available for monkeypox, and it is important to get vaccinated if you are traveling to an area where monkeypox is found.